Using the RNSA
Access the Jupyter notebook with the code available here!
Run notebook online via Binder:
Importing the Real-Valued Negative Selection Algorithm.
from aisp.nsa import RNSA
Generating dice bubbles for classes randomly.
Using the make_blobs function, two sets of data are generated in the form of bubbles, in the range between 0 and 1, representing each class x and y. Then this data is separated into test and training sets.
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Generating the samples and outputs for the training.
samples, output = make_blobs(n_samples=500 , n_features=2, cluster_std=0.07, center_box=([0.0, 1.0]), centers=[[0.25, 0.75], [0.75, 0.25]], random_state=1234)
# Separating data for training and testing.
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(samples, output, test_size=0.2)
Testing the model default-NSA:
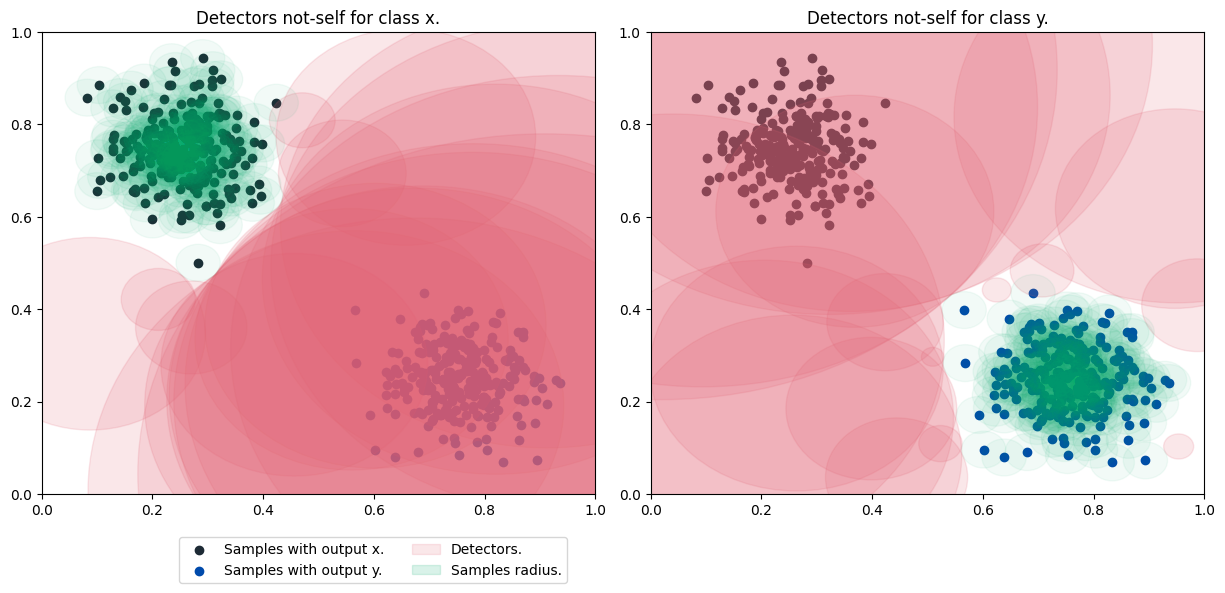
Start the model with 500 detectors, each with a radius of 0.06. Then, it presents the result of the forecast accuracy.
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report, accuracy_score
# Starting the class.
model = RNSA(N=500, r=0.05, seed=1234)
# Carrying out the training:
model.fit(X=train_x, y=train_y)
# Previewing classes with test samples.
prev_y = model.predict(test_x)
# Showing the accuracy of predictions for actual data.
print(f"The accuracy is {accuracy_score(prev_y, test_y)}")
print(classification_report(test_y, prev_y))
Output:
✔ Non-self detectors for classes (0, 1) successfully generated: ┇██████████┇ 1000/1000 detectors
The accuracy is 1.0
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 55
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 45
accuracy 1.00 100
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 100
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 100
Detector and sample plotting:
Testing the model V-detector:
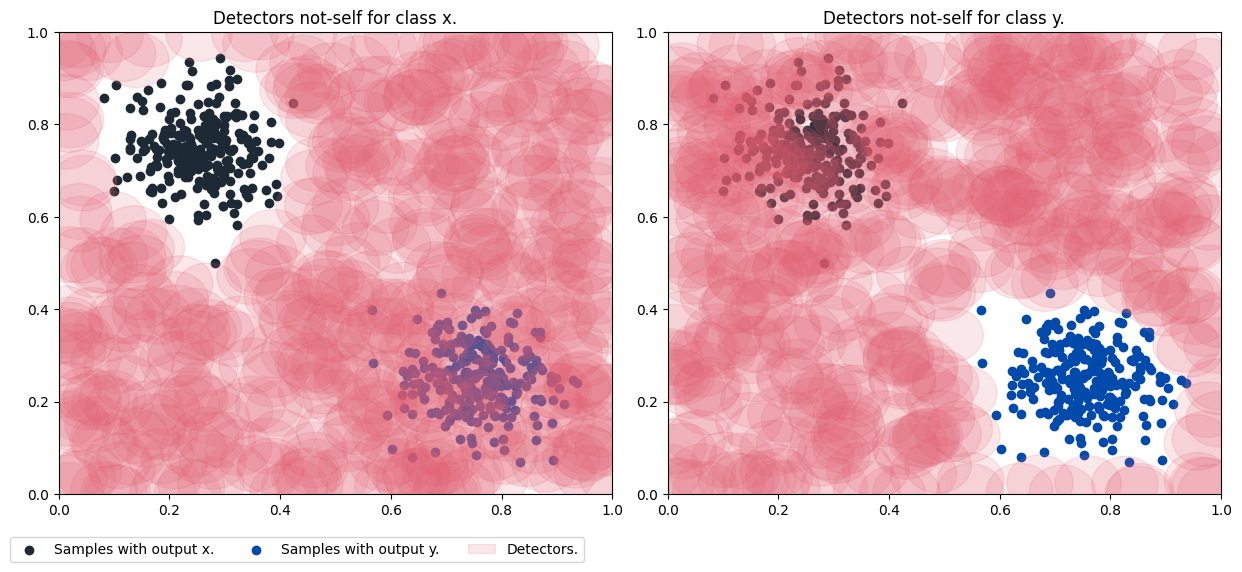
Start the model with 50 detectors, where the minimum radius is 0.05 and the sample's own radius is 0.04. It then shows the forecast accuracy result.
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report, accuracy_score
# Starting the class.
model = RNSA(N=20, r=0.02, algorithm='V-detector', r_s=0.04, seed=123)
# Carrying out the training:
model.fit(X=train_x, y=train_y)
# Previewing classes with test samples.
prev_y = model.predict(test_x)
# Showing the accuracy of predictions for actual data.
print(f"The accuracy is {accuracy_score(prev_y, test_y)}")
print(classification_report(test_y, prev_y))
Output:
✔ Non-self detectors for classes (0, 1) successfully generated: ┇██████████┇ 40/40 detectors
The accuracy is 1.0
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 55
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 45
accuracy 1.00 100
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 100
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 100
Detector and sample plotting: